How it works
Voltaren Emulgel Back & Muscle Pain with a No Mess Applicator contains a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) called diclofenac, a pain reliever. This gel relieves pain at its source. The gel works by blocking production of some of the body’s chemicals that cause swelling (inflammation), pain and tenderness¹. Voltaren Emulgel Back & Muscle Pain has shown to be effective in providing pain relief and reducing inflammation.
The active ingredient in Voltaren Emulgel Back & Muscle Pain, diclofenac, has been used as a pain reliever for many years across the world. ...The Emulgel formula provides both the benefits of a moisturising cream and a cooling gel.
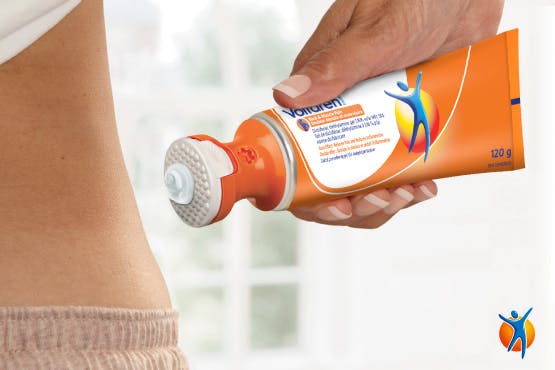
1. To remove the seal before first use, remove the transparent protective cover and then unscrew the applicator cap. Use the star-shape groove (the key) located at the side of the applicator cap to remove the security seal (star seal) of the tube. Screw the applicator cap back on the tube before dispensing the gel.
2. To open, simply pull the white part of the applicator cap. Gently squeeze the tube to push the gel to the surface of the applicator cap. Use the applicator-capped tube as you would use your fingers to gently and slowly rub the gel into the skin on the affected area. The slight pressure of rubbing in the gel will automatically close the applicator cap. You may notice a slight cooling effect when you rub the gel in.
3. After use, clean the applicator cap with cotton towel or tissue until visually dry and clean. Do not immerse or rinse under water. Do not use any solvent or detergent to clean the surface of the applicator cap. After cleaning, place the transparent protective cap back on the tube before storage. Do not reuse the applicator cap with another tube. Discard the tube with its applicator cap following the recommended procedure for the disposal of any medication.
4. After application wipe your hands with a tissue and then wash to avoid accidental contact with the mouth and eyes. The tissue should be thrown in the trash after use.
5. Wait until Voltaren Emulgel Back & Muscle Pain dries before showering or bathing.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater (e.g. toilet or sink). Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help to protect the environment.
Usual dose:
For adults and adolescents 16 years and older (regular strength):
- Apply gel 3 to 4 times a day on the affected area.
- The amount needed will vary depending upon the size of the painful or swollen area: 2 g to 4 g (1 g equals a strip approximately 2 cm long) gel will be sufficient to cover a 400 to 800 cm2 area.
- Do not use more than 4 times in 24 hours.
Use no more than is required for the shortest period of time needed. The gel should not be used for mor than 7 days for muscle and joint injuries unless recommended by a doctor. Talk to your doctor if your condition does not improve within 7 days, or if it gets worse.
Contains diclofenac diethylamine 1.16% w/w. To be sure this product is right for you always read and follow the label.

Active Ingredient: Diclofenac diethylamine 1.16% w/w. To be sure this product is right for you always read and follow the label.
Refer to the leaflet for warnings & precautions. Always read the enclosed insert before use to check if this product is suitable for you.
Refer to leaflet for dosage information.
To be sure the product is right for you, always read and follow the label.
Health, wellness & your pain
Pain is rarely just physical nor is it always solved by taking medicine alone. Voltaren is your ally in helping you take more control of your pain journey, from the way to sleep, to what you eat, mental wellbeing and complementary pain relief therapies.